Configuring the Gradio Web User Interface for Access
After all the resources have been configured within the Ray Serve Cluster, it's now time to directly access the Llama2 chatbot. The web interface is powered by the Gradio UI.
You can learn more about Load Balancers in the Load Balancer module provided in this workshop.
Deploying Gradio Web User Interface
Once the AWS Load Balancer Controller has been installed, we can deploy the Gradio UI components.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: gradio-llama2-inf2
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: gradio-deployment
namespace: gradio-llama2-inf2
labels:
app: gradio
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: gradio
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: gradio
spec:
containers:
- name: gradio
image: public.ecr.aws/data-on-eks/gradio-web-app-base:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 7860
resources:
requests:
cpu: "512m"
memory: "2048Mi"
limits:
cpu: "1"
memory: "4096Mi"
env:
- name: MODEL_ENDPOINT
value: "/infer"
- name: SERVICE_NAME
value: "http://llama2-serve-svc.llama2.svc.cluster.local:8000"
volumeMounts:
- name: gradio-app-script
mountPath: /app/gradio-app.py
subPath: gradio-app-llama2-inf2.py
volumes:
- name: gradio-app-script
configMap:
name: gradio-app-script
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: gradio-service
namespace: gradio-llama2-inf2
annotations:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-type: external
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-scheme: internet-facing
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-nlb-target-type: ip
spec:
selector:
app: gradio
ports:
- name: http
protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 7860
type: LoadBalancer
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: gradio-app-script
namespace: gradio-llama2-inf2
data:
gradio-app-llama2-inf2.py: |
import gradio as gr
import requests
import os
# Constants for model endpoint and service name
model_endpoint = "/infer"
service_name = os.environ.get("SERVICE_NAME", "http://localhost:8000")
# Function to generate text
def text_generation(message, history):
prompt = message
# Create the URL for the inference
url = f"{service_name}{model_endpoint}"
try:
# Send the request to the model service
response = requests.get(url, params={"sentence": prompt}, timeout=180)
response.raise_for_status() # Raise an exception for HTTP errors
full_output = response.json()[0]
# Removing the original question from the output
answer_only = full_output.replace(prompt, "", 1).strip('["]?\n')
# Safety filter to remove harmful or inappropriate content
answer_only = filter_harmful_content(answer_only)
return answer_only
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
# Handle any request exceptions (e.g., connection errors)
return f"AI: Error: {str(e)}"
# Define the safety filter function (you can implement this as needed)
def filter_harmful_content(text):
# TODO: Implement a safety filter to remove any harmful or inappropriate content from the text
# For now, simply return the text as-is
return text
# Define the Gradio ChatInterface
chat_interface = gr.ChatInterface(
text_generation,
chatbot=gr.Chatbot(line_breaks=True),
textbox=gr.Textbox(placeholder="Ask me a question", container=False, scale=7),
title="Llama2/3 AI Chat",
description="Ask me any question",
theme="soft",
examples=["How many languages are in India", "What is Generative AI?"],
cache_examples=False,
retry_btn=None,
undo_btn="Delete Previous",
clear_btn="Clear",
)
# Launch the ChatInterface
chat_interface.launch(server_name="0.0.0.0")
The components consist of a Deployment, Service, and ConfigMap to launch the application. In particular, the Service component is named gradio-service and is deployed as a LoadBalancer.
namespace/gradio-llama2-inf2 created
configmap/gradio-app-script created
service/gradio-service created
deployment.apps/gradio-deployment created
To check the status of each component, run the following commands:
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
gradio-deployment 1/1 1 1 95s
NAME DATA AGE
gradio-app-script 1 110s
kube-root-ca.crt 1 111s
Accessing the Chatbot Website
Once the load balancer has finished deploying, use the external IP address to directly access the website:
NAME TYPE ClUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
gradio-service LoadBalancer 172.20.84.26 k8s-gradioll-gradiose-a6d0b586ce-06885d584b38b400.elb.us-west-2.amazonaws.com 80:30802/TCP 8m42s
To wait until the Network Load Balancer has finished provisioning, run the following command:
Now that our application is exposed to the outside world, let's access it by pasting the URL in your web browser. You will see the Llama2 chatbot and will be able to interact with it by asking questions.
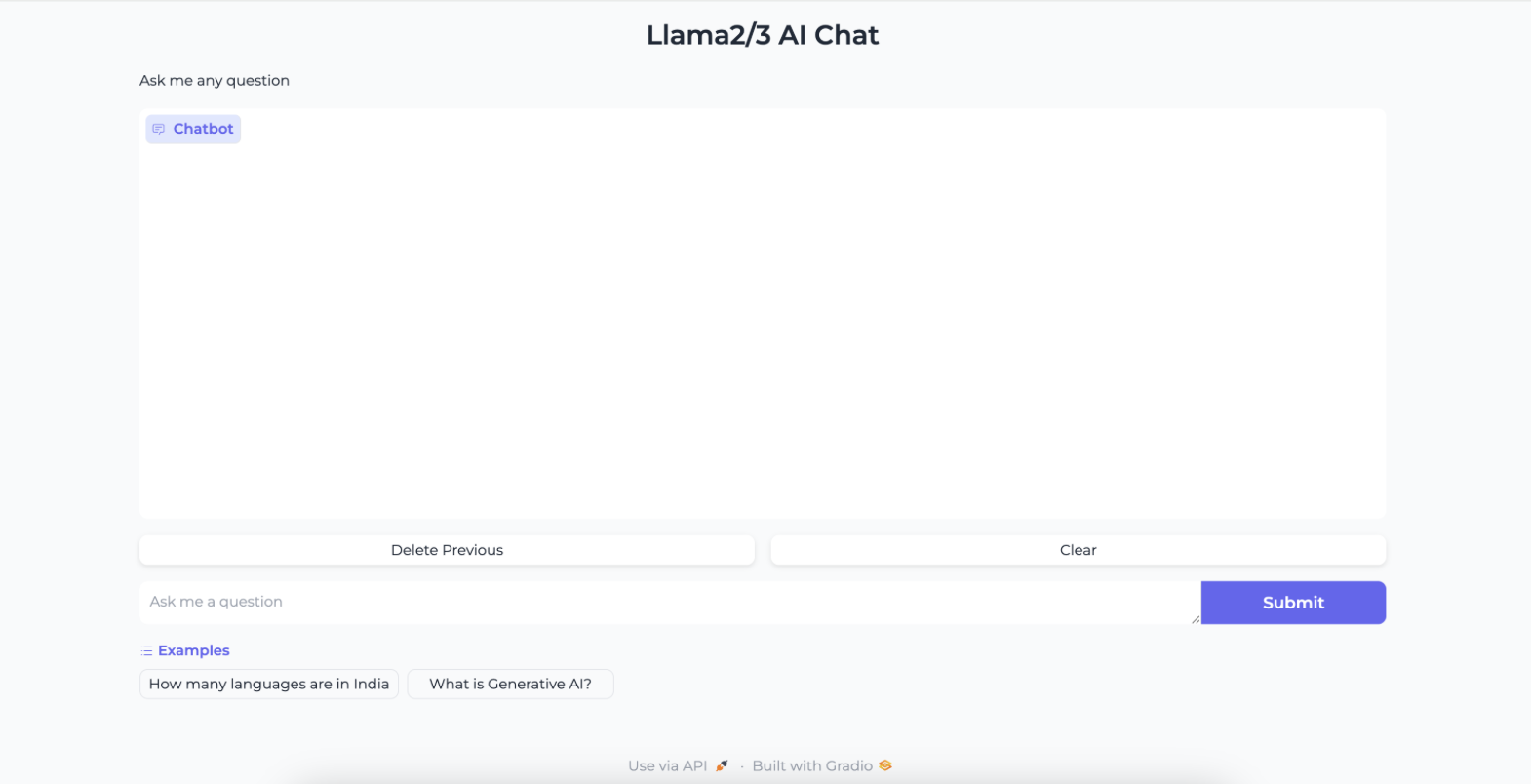
This concludes the current lab on deploying the Meta Llama-2-13b Chatbot Model within an EKS Cluster via Karpenter.